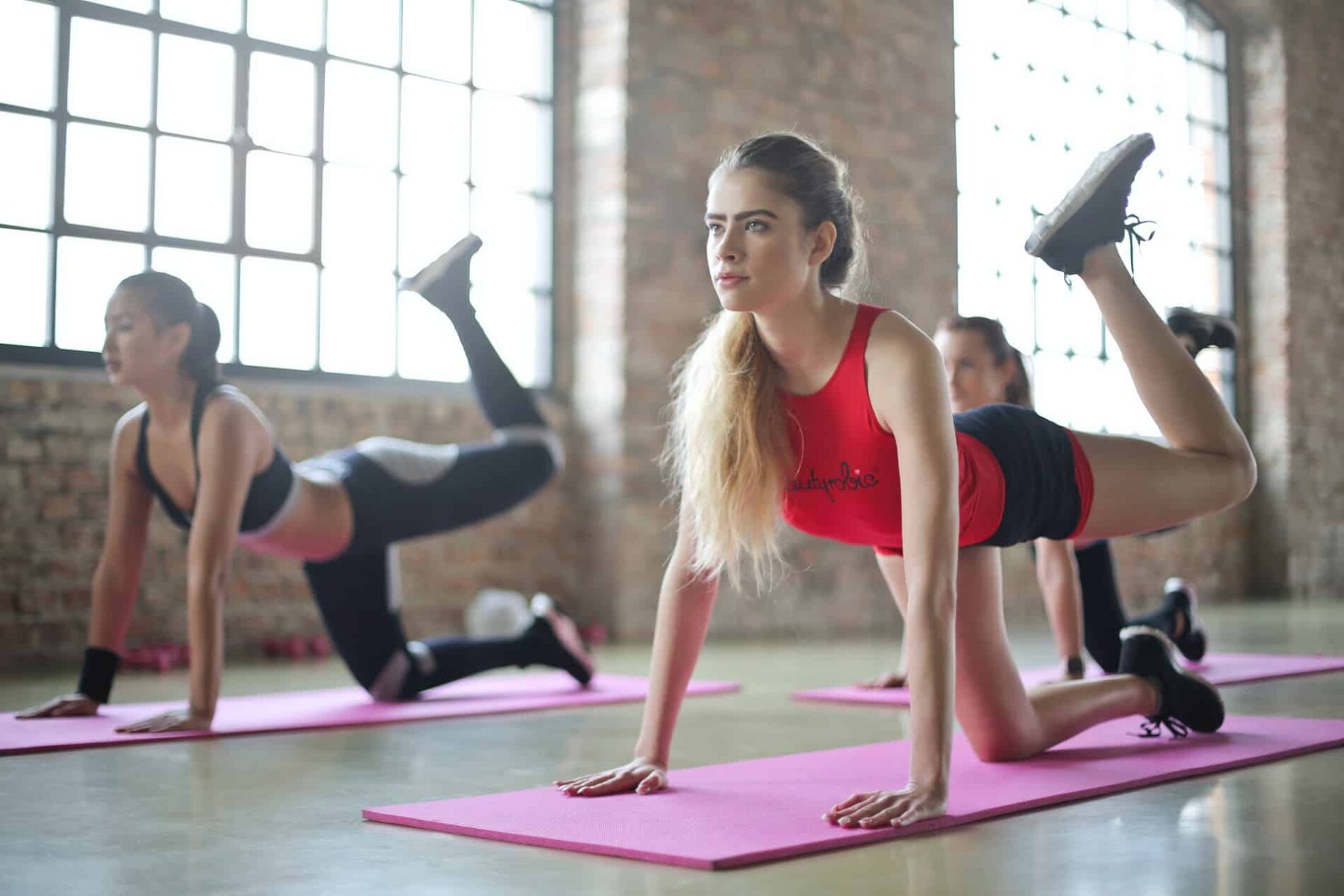
Pilates is known as a core-developing mode of exercise used across the fitness spectrum, from casual fitness enthusiasts to professional athletes. Its main principle is to maximize core strength for better balance, stability, mobility, and strength. However, Pilates has another health benefit that many people may not know.
Pilates helps in improving digestion by stimulating and massaging the digestive tract in the stomach area. The twist movements, in particular, introduce physical stress to the muscles along the abdominal area in multiple directions, making it ideal for increasing intestinal contractions.
This article will explain the process of digestion to aid in understanding how exercise can affect digestion. It will also explain how Pilates, as a form of anaerobic exercise, can help promote better digestion safely without risking intestinal injuries. Lastly, it will explain several Pilates exercises that are effective at stimulating and massaging the digestive tract along the abdominal area.
The Digestive Process
The digestive system is composed of the organs of the digestive tract namely, the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and the anus. Other organs like the tongue, liver, and pancreas help in digesting food.
It is important to maintain good digestion because it is responsible for supplying energy and nourishing the cells within the body. Without good digestion, an individual can experience lethargy, irregular bowel movement, stress, hormonal imbalance, nutrient deficiency, and weight gain. Furthermore, bad digestion can fail to eliminate harmful toxins in the body and can cause digestive disorders.

It is estimated that around 70% of the body’s immune system is located along the digestive tract. As such, the digestive system is often considered as a subset of the body’s immune system, functioning as a physical shield against pathogens.
The gut, or the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, composed mainly of the digestive tract, is commonly referred to as the second brain. The health of the GI tract can also affect other bodily functions. Thus, maintaining good gut health can also improve overall well-being.
Good gut health requires maintaining a good gut microbiome or the ecosystem of microorganisms that helps the body digest food. The gut microbiome has over 1000 different bacteria species that are responsible for combating dangerous microorganisms and promoting good digestive functions. It must have a good balance between good and bad gut bacteria to reduce intestinal permeability, which can cause digestive discomfort and disorder.
Relationship Between Exercise and Digestion
Exercise affects digestion by producing stress to the digestive tract, prompting it to transition from its parasympathetic state where the stomach builds an acidic environment with digestive enzymes and mucous conducive for food digestion. It also improves intestinal flow by increasing the blood to the stomach for better digestion.
Dr. Kavin Nanda, a Gastroenterologist, notes that regular exercise can improve gut health and fortify the digestive tract over time by improving the microbiome in the digestive tract to facilitate digestion. It also cultivates stronger digestive enzymes and better intestinal contractions to improve overall circulation in the digestive tract.
Furthermore, exercise can enhance metabolism for faster burning of calories as it stimulates the digestive tract to work harder. However, metabolism only increases during workouts and reverts to its resting state afterward.

It can also increase insulin response to encourage the cells to absorb and expend rather than resist glucose in the body for supplementary energy. This is beneficial for people who are prone to developing Type 2 diabetes.
It also stimulates the release of endorphins or mood hormones and reduces the production of the stress hormone, cortisol. This also affects digestion since psychological stress is known to cause digestive issues.
Lastly, it can improve regular bowel movement as the increased blood circulation improves the intestinal transit time through the improvement of peristalsis or the muscle contraction of the digestive tract.
Heavy Exercise vs Light Exercise
Not all exercises are good and beneficial for the digestive process. Extremely active individuals can also suffer from digestive issues. While sedentary individuals can suffer from bloating and constipation, extremely active individuals can suffer from intestinal injury, especially if the digestive process is still underway when doing exercise.
Heavy exercise with an ongoing digestive process diverts the blood flow from the digestive tract to the heart and the muscles. This introduces undue stress to the digestive tract, especially when digesting high-fat and high-protein foods.
Light exercise is often the most effective form of exercise in promoting good digestion. Brisk walking is known to enhance intestinal contractility which helps in promoting a regular bowel movement. Abdominal stretches can also improve intestinal contractions for better digestion.
Furthermore, light exercise can also help eliminate heartburn and stomach cramps as a result of a sedentary lifestyle. However, these exercises must still be timed correctly to avoid undue stress for the digestive tract. It is often recommended to take at least 2 hours of rest to digest before exercising after eating high-fat and high-protein foods to reduce the risk of digestive issues.
Pilates Aiding Digestion

Pilates is a form of anaerobic exercise that focuses primarily on exercising the abdominal region. As shown previously, abdominal workouts can promote better digestion by improving intestinal contraction or peristalsis.
The focus of Pilates exercises on the abdominal region can help stimulate the digestive tract and eliminate digestive issues such as bloating and constipation. The stretching and relaxation of abdominal muscles can also help prevent hyperacidity. Twisting exercises, in particular, help eliminate digestive issues caused by stale air and gas in the stomach.
Unlike strenuous workouts, Pilates exercises introduce an appropriate amount of stress that will not overexert pressure to the digestive tract that can cause digestive issues. Furthermore, the engagement of the deep core muscles stabilizes the core and balances the pressure through the entire core region. The activation of the deep core muscles is often missing in normal sit-ups and crunches.
Pilates exercises also relax the psoas muscle which runs from the upper thigh, stomach, and then towards the lumbar spine. Relaxing this specific muscle can help in massaging the digestive tract during twist movements in Pilates exercises.
Breathing is another essential component of Pilates exercises which aids in reducing incidences of digestive stress such as bloating and heartburn. Deep breathing in Pilates uses the stomach muscles to massage and relieve the digestive tract and stimulate the diaphragm muscles. It also stretches the digestive organs within the abdominal region which helps in releasing intestinal toxins.
Pilates Exercises that Help in Digestion
Twist movements are the best types of Pilates movements for stimulating the digestive tract. The Criss-cross exercise is one of the most popular twist exercises in Pilates intended to target the oblique abdominals. It is one of the best Pilates exercises for stimulating the digestive tract because it mainly focuses on the abdominal area between the pelvis and the ribcage where digestion mostly occurs.
The Criss-Cross exercise starts from a supine position where the hands are placed behind the head. The individual will then twist the upper body towards either side while curling the upper body towards the knees. This must be performed with proper breathing of around 8-10 breathing repetitions per side.
The Saw exercise is another twist movement in Pilates that also exercises the traverse abdominals and obliques. This exercise involves sitting on the mat, forming a V shape with the legs, and a T shape with the arms. Then, the individual will twist the body towards either side and will touch the pinky toe with the pinky finger while maintaining the T shape of the arms. Doing this exercise correctly with proper breathing will put pressure on the abdominal area and engage and massage the digestive tract.
The Roll-up is another Pilates exercise that incorporates a lot of abdominal engagement. This exercise starts from a supine position and then raising the arms towards the ceiling. Afterward, the individual must lift the upper body using the abdominal muscles until the arms and legs are parallel and the body forms a C-shaped figure. Unlike twist movements, this exercise involves drawing strength from the abdominal muscles which massages the digestive tract in the stomach area effectively.
It is also helpful to use a medicine ball to perform restorative movements which involve placing the medicine ball on the back along the pelvic area and rolling the body up and down the medicine ball. This exercise will also massage the digestive tract and stimulate digestion or relieve stale air that can cause bloating.
Conclusion
Pilates workouts are highly effective not only in targeting deep, traverse abdominal muscles but also stimulating the digestive organs along the abdominal region. Using combinations of various Pilates exercises to massage the digestive tract in the stomach as well as light exercises such as walks can help improve digestion and avoid digestive issues associated with a sedentary lifestyle.






















What do you think?